This chapter describes the central set of read-only reference tables and views of each Oracle database, known collectively as the data dictionary.
- Info The User Does Not Have Rsop Data Recovery
- Info The User Does Not Have Rsop Data Collected
- Info The User Does Not Have Rsop Data Breaches
- Info The User Does Not Have Rsop Data Management System
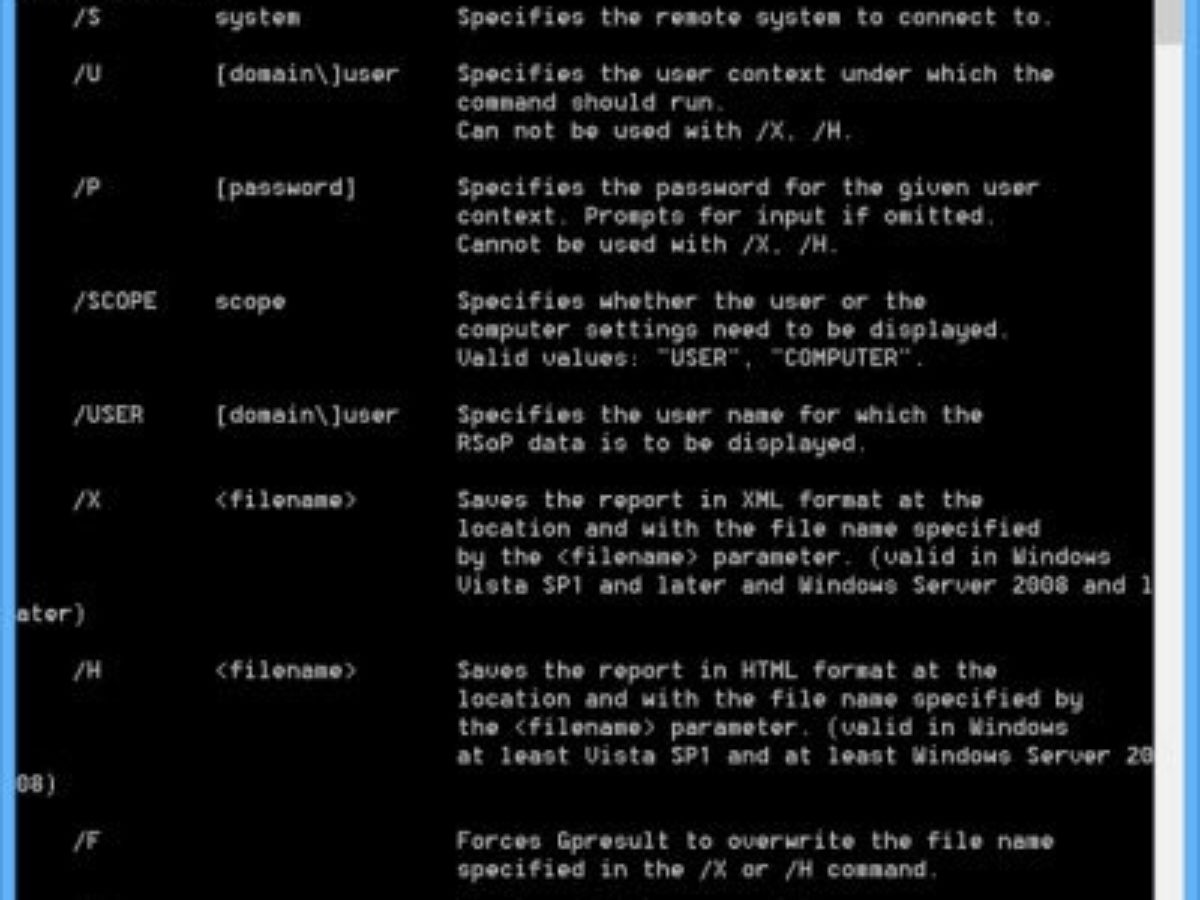
Save RSOP Information to an HTML File Saves resultant set of policy information to an HTML file. This script, contributed by Mike Stephens of Microsoft, requires the Group Policy Management Console. Data do not have to be deleted. Your company/organisation runs an online newspaper. One of your journalists publishes a story on how a politician had laundered money in off-shore banks. The politician requests to remove the story because his personal data is being processed. INFO: The user 'DOMAIN user' does not have RSOP data When I run rsop.msc, I get the following error RSoP data is invalid. Likely causes are, data is corrupt, data has been deleted or data has never been created. Jan 31, 2013 INFO: The user does not have RSoP data. Click to expand. I don't know what changed on the network or in GPOs to do this, but I have no doubt some consultant (whom I don't even know of, working through a consultant co-worker) did something.
This chapter contains the following topics:
Introduction to the Data Dictionary
One of the most important parts of an Oracle database is its data dictionary, which is a read-only set of tables that provides information about the database. A data dictionary contains:
The definitions of all schema objects in the database (tables, views, indexes, clusters, synonyms, sequences, procedures, functions, packages, triggers, and so on)
How much space has been allocated for, and is currently used by, the schema objects
Default values for columns
Integrity constraint information
The names of Oracle users
Privileges and roles each user has been granted
Auditing information, such as who has accessed or updated various schema objects
Other general database information
The data dictionary is structured in tables and views, just like other database data. All the data dictionary tables and views for a given database are stored in that database's SYSTEM tablespace.
Not only is the data dictionary central to every Oracle database, it is an important tool for all users, from end users to application designers and database administrators. Use SQL statements to access the data dictionary. Because the data dictionary is read only, you can issue only queries (SELECT statements) against it's tables and views.
See Also:
'Bigfile Tablespaces' for more information aboutSYSTEM tablespacesStructure of the Data Dictionary
The data dictionary consists of the following:
Base Tables
The underlying tables that store information about the associated database. Only Oracle should write to and read these tables. Users rarely access them directly because they are normalized, and most of the data is stored in a cryptic format.
User-Accessible Views
The views that summarize and display the information stored in the base tables of the data dictionary. These views decode the base table data into useful information, such as user or table names, using joins and WHERE clauses to simplify the information. Most users are given access to the views rather than the base tables.
SYS, Owner of the Data Dictionary
The Oracle user SYS owns all base tables and user-accessible views of the data dictionary. No Oracle user should ever alter (UPDATE, DELETE, or INSERT) any rows or schema objects contained in the SYS schema, because such activity can compromise data integrity. The security administrator must keep strict control of this central account.
Caution:
Altering or manipulating the data in data dictionary tables can permanently and detrimentally affect the operation of a database.
How the Data Dictionary Is Used
The data dictionary has three primary uses:
Oracle accesses the data dictionary to find information about users, schema objects, and storage structures.
Oracle modifies the data dictionary every time that a data definition language (DDL) statement is issued.
Any Oracle user can use the data dictionary as a read-only reference for information about the database.
How Oracle Uses the Data Dictionary
Data in the base tables of the data dictionary is necessary for Oracle to function. Therefore, only Oracle should write or change data dictionary information. Oracle provides scripts to modify the data dictionary tables when a database is upgraded or downgraded.
Caution:
No data in any data dictionary table should be altered or deleted by any user.During database operation, Oracle reads the data dictionary to ascertain that schema objects exist and that users have proper access to them. Oracle also updates the data dictionary continuously to reflect changes in database structures, auditing, grants, and data.
For example, if user Kathy creates a table named parts, then new rows are added to the data dictionary that reflect the new table, columns, segment, extents, and the privileges that Kathy has on the table. This new information is then visible the next time the dictionary views are queried.
Public Synonyms for Data Dictionary Views
Oracle creates public synonyms for many data dictionary views so users can access them conveniently. The security administrator can also create additional public synonyms for schema objects that are used systemwide. Users should avoid naming their own schema objects with the same names as those used for public synonyms.
Cache the Data Dictionary for Fast Access
Much of the data dictionary information is kept in the SGA in the dictionary cache, because Oracle constantly accesses the data dictionary during database operation to validate user access and to verify the state of schema objects. All information is stored in memory using the least recently used (LRU) algorithm.
Parsing information is typically kept in the caches. The COMMENTS columns describing the tables and their columns are not cached unless they are accessed frequently.
Other Programs and the Data Dictionary
Other Oracle products can reference existing views and create additional data dictionary tables or views of their own. Application developers who write programs that refer to the data dictionary should refer to the public synonyms rather than the underlying tables: the synonyms are less likely to change between software releases.
How to Use the Data Dictionary
The views of the data dictionary serve as a reference for all database users. Access the data dictionary views with SQL statements. Some views are accessible to all Oracle users, and others are intended for database administrators only.
The data dictionary is always available when the database is open. It resides in the SYSTEM tablespace, which is always online.
The data dictionary consists of sets of views. In many cases, a set consists of three views containing similar information and distinguished from each other by their prefixes:
Table 7-1 Data Dictionary View Prefixes
| Prefix | Scope |
|---|---|
| User's view (what is in the user's schema) |
| Expanded user's view (what the user can access) |
| Database administrator's view (what is in all users' schemas) |
The set of columns is identical across views, with these exceptions:
Views with the prefix
USERusually exclude the columnOWNER. This column is implied in theUSERviews to be the user issuing the query.Some
DBAviews have additional columns containing information useful to the administrator.See Also:
Oracle Database Reference for a complete list of data dictionary views and their columns
Views with the Prefix USER
The views most likely to be of interest to typical database users are those with the prefix USER. These views:
Refer to the user's own private environment in the database, including information about schema objects created by the user, grants made by the user, and so on
Display only rows pertinent to the user
Have columns identical to the other views, except that the column
OWNERis impliedReturn a subset of the information in the
ALLviewsCan have abbreviated
PUBLICsynonyms for convenience
For example, the following query returns all the objects contained in your schema:
Views with the Prefix ALL
Views with the prefix ALL refer to the user's overall perspective of the database. These views return information about schema objects to which the user has access through public or explicit grants of privileges and roles, in addition to schema objects that the user owns. For example, the following query returns information about all the objects to which you have access:
Views with the Prefix DBA
Views with the prefix DBA show a global view of the entire database. Synonyms are not created for these views, because DBA views should be queried only by administrators. Therefore, to query the DBA views, administrators must prefix the view name with its owner, SYS, as in the following:
Oracle recommends that you implement data dictionary protection to prevent users having the ANY system privileges from using such privileges on the data dictionary. If you enable dictionary protection (O7_DICTIONARY_ACCESSIBILITY is false), then access to objects in the SYS schema (dictionary objects) is restricted to users with the SYS schema. These users are SYS and those who connect as SYSDBA.

See Also:
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for detailed information on system privileges restrictions
The DUAL Table
The table named DUAL is a small table in the data dictionary that Oracle and user-written programs can reference to guarantee a known result. This table has one column called DUMMY and one row containing the value X.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Reference for more information about theDUAL tableDynamic Performance Tables
Throughout its operation, Oracle maintains a set of virtual tables that record current database activity. These tables are called dynamic performance tables.
Dynamic performance tables are not true tables, and they should not be accessed by most users. However, database administrators can query and create views on the tables and grant access to those views to other users. These views are sometimes called fixed views because they cannot be altered or removed by the database administrator.
SYS owns the dynamic performance tables; their names all begin with V_$. Views are created on these tables, and then public synonyms are created for the views. The synonym names begin with V$. For example, the V$DATAFILE view contains information about the database's datafiles, and the V$FIXED_TABLE view contains information about all of the dynamic performance tables and views in the database.
See Also:
Oracle Database ReferenceInfo The User Does Not Have Rsop Data Recovery
for a complete list of the dynamic performance views' synonyms and their columnsInfo The User Does Not Have Rsop Data Collected
Database Object Metadata
Info The User Does Not Have Rsop Data Breaches
The DBMS_METADATA package provides interfaces for extracting complete definitions of database objects. The definitions can be expressed either as XML or as SQL DDL. Two styles of interface are provided:
Info The User Does Not Have Rsop Data Management System
A flexible, sophisticated interface for programmatic control
A simplified interface for ad hoc querying
See Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for more information aboutDBMS_METADATA
