When you think of indenting information, you normally think of a word processor. It is not unusual to indent paragraphs or specific lines of information on the screen. Excel, while definitely not a word processor, allows you to easily indent information within a cell.
Easiest way I found is to right-click on the Indent button and Add to Quick Access Toolbar. After that, press the ALT key to see which numeral was assigned to it (order of buttons at the top, so changeable as you please) and my Excel 2013 gave it the ALT-4 shortcut.
To set the indent to be used in a cell, follow these steps:

- Select the cells you want to format.
- Choose Cells from the Format menu. Excel displays the Format Cells dialog box.
- Make sure the Alignment tab is selected. (See Figure 1.)
- Using the Indent control, specify the number of characters by which the cell contents should be indented. You can pick any whole number between 0 and 15.
- Click on OK.
Figure 1. The Alignment tab of the Format Cells dialog box.
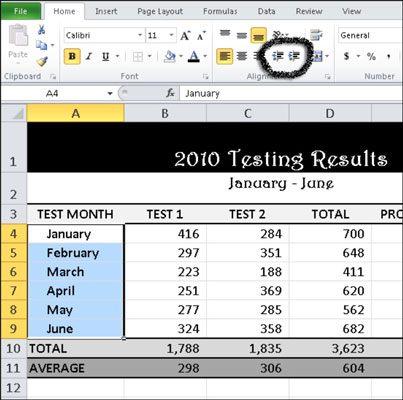
- Indent text in a cell. In Microsoft Excel, the Tab key does not indent text in a cell like it does, say, in Microsoft Word; it just moves the pointer to the next cell. To change the indentation of the cell contents, use the Indent icons that reside right underneath the Orientation button. To move text further to the right, click the Increase.
- Select the cells containing text you want to indent. Click the Increase Indent button in the Alignment group on the Home tab. Each time you click the Increase Indent button, Excel adds a small amount of.
- For extra space between cell text and the left or right cell border, click “Left (Indent)” or “Right (Indent).” Click “Distributed (Indent)” to have equal spacing between both the text and the cell borders on both sides. In the “Indent” box, select the size of your additional spacing.
Each number of indent moves the contents of the cell about one character width to the right. (There goes that strange character measurement system in Excel again.) You can also control the indentation of cell contents by using the two indent tools on the Formatting toolbar. Each click of a tool moves the cell contents one position to the left or right.
If you have set up a cell so that text wraps within the cell, then indentation affects all the lines of text within the cell—not just the first line.
When you think of indenting information, you normally think of a word processor. It is not unusual to indent paragraphs or specific lines of information on the screen. Excel, while definitely not a word processor, allows you to easily indent information within a cell.
To set the indent to be used in a cell, follow these steps:
- Select the cells you want to format.
- Choose Cells from the Format menu. Excel displays the Format Cells dialog box.
- Make sure the Alignment tab is selected. (See Figure 1.)
- Using the Indent control, specify the number of characters by which the cell contents should be indented. You can pick any whole number between 0 and 15.
- Click on OK.
Figure 1. The Alignment tab of the Format Cells dialog box.
Each number of indent moves the contents of the cell about one character width to the right. (There goes that strange character measurement system in Excel again.) You can also control the indentation of cell contents by using the two indent tools on the Formatting toolbar. Each click of a tool moves the cell contents one position to the left or right.
Hanging Indents In Excel
If you have set up a cell so that text wraps within the cell, then indentation affects all the lines of text within the cell—not just the first line.
